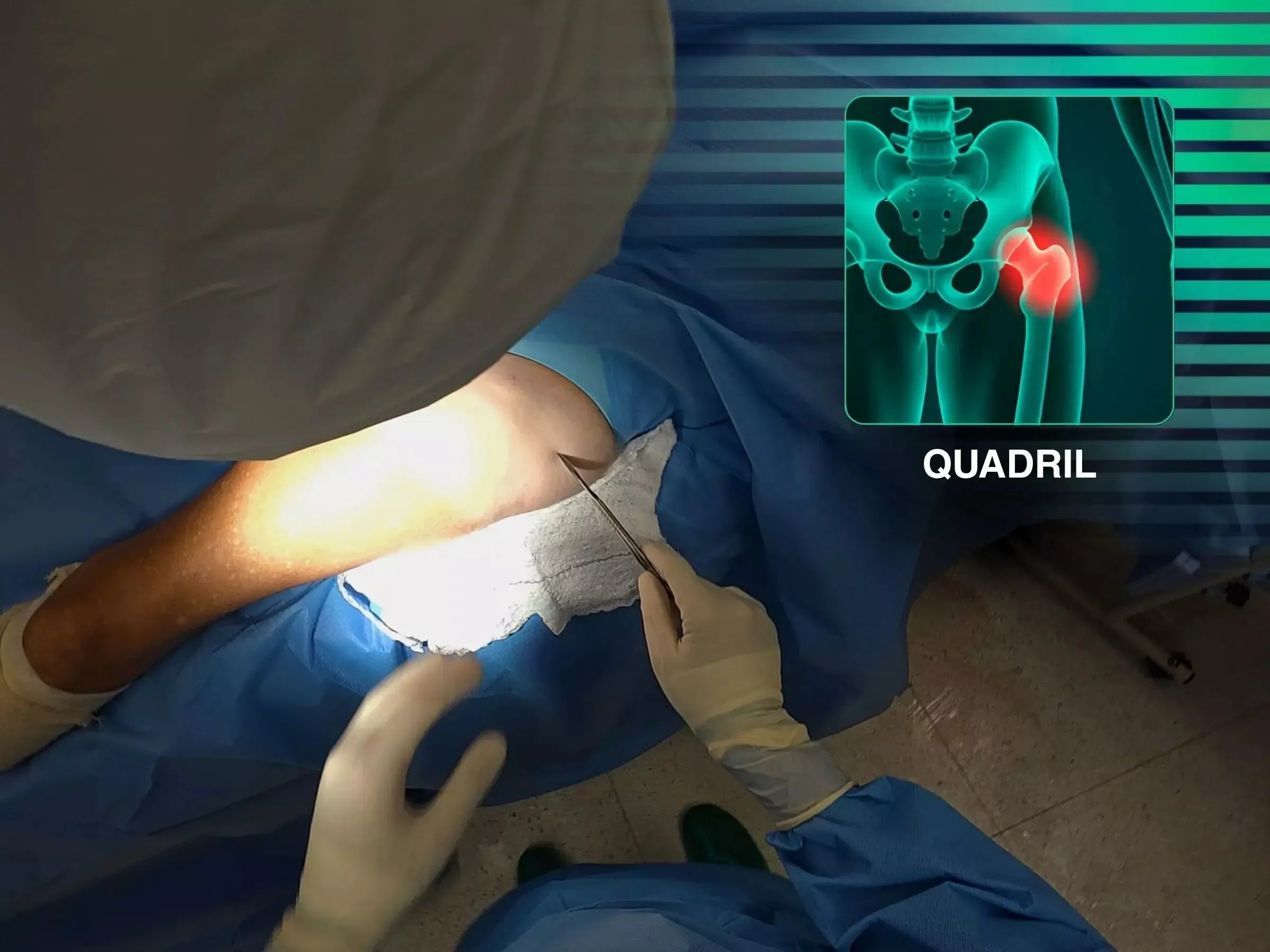
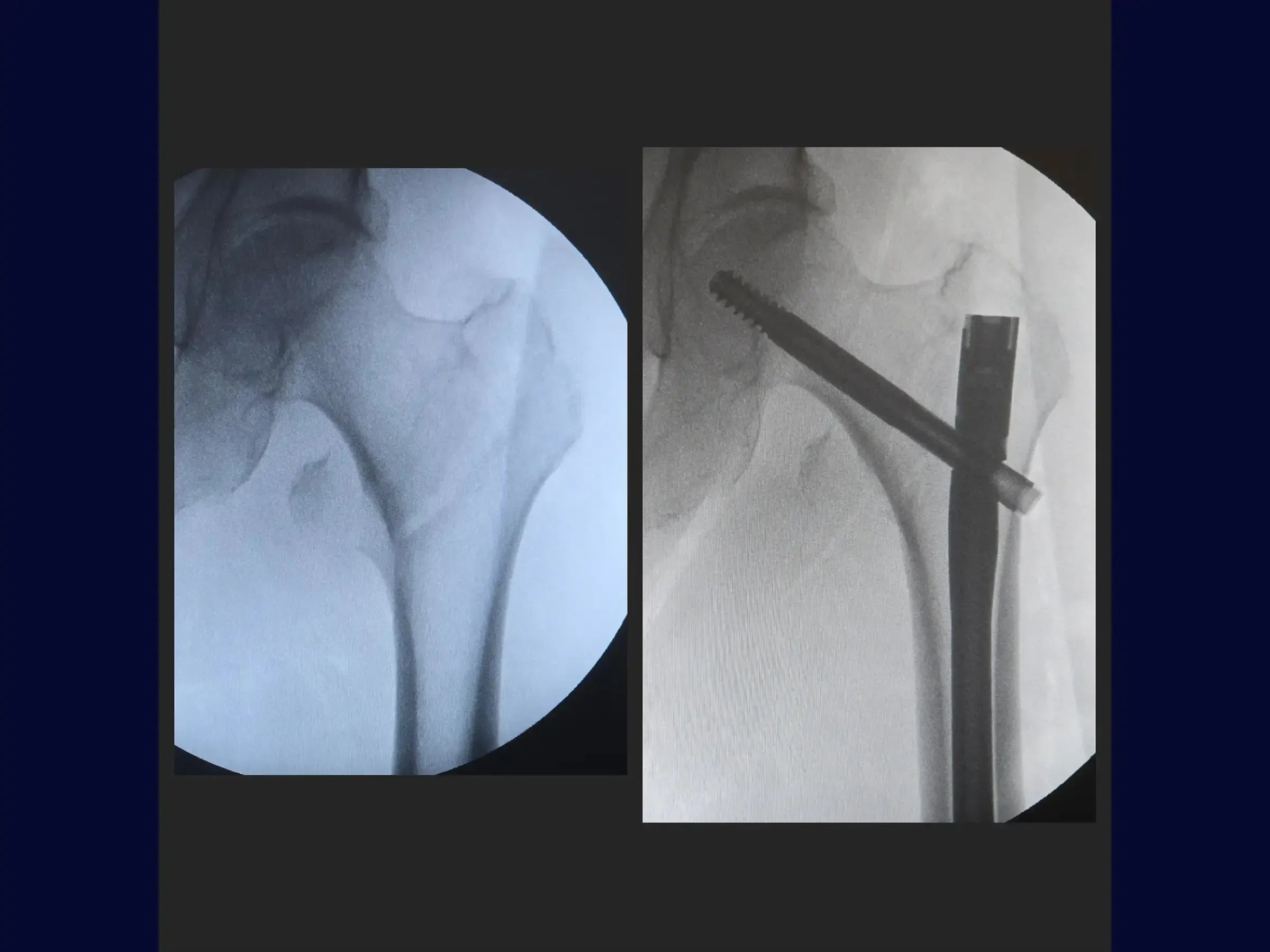
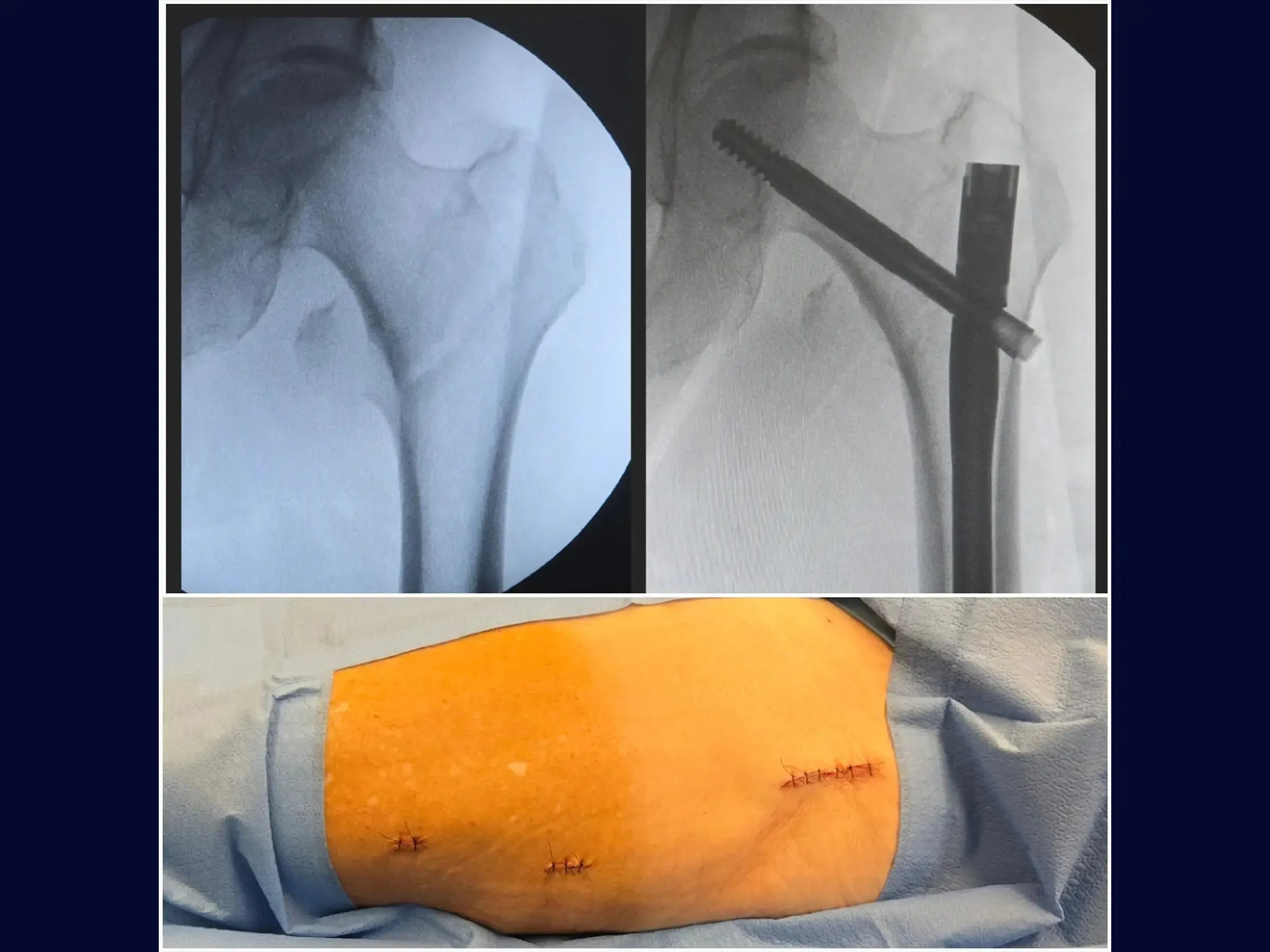
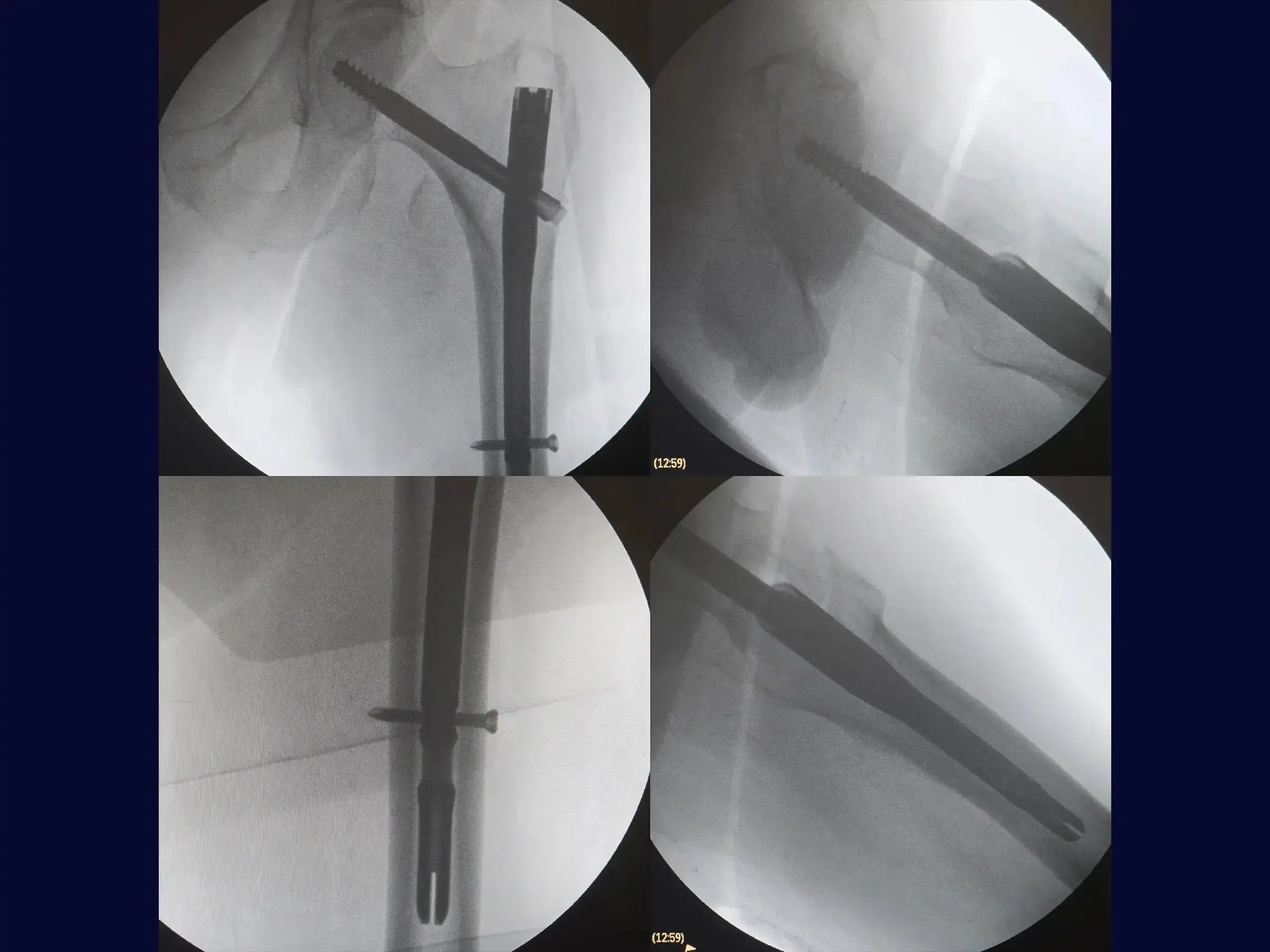
Transtrochanteric Fracture with Intramedullary Nail (Without Traction Table)
Intramedullary Nail without Traction: Enhance the technique and accelerate recovery in femur fractures.


4k videos
Professional Dubbing
Escolher opções







Description
Master the surgical treatment of intertrochanteric femur fractures with intramedullary nail, now without the need for a traction table. This training offers a practical immersion in the precision of locating the guide wire entry point, optimizing positioning in the lateral view with a parallelism guide, and the technique for fixing sliding and locking screws. The goal is to provide a less invasive approach that allows for early weight-bearing and a favorable prognosis for the elderly patient.
Training Focus:
- Treatment of intertrochanteric femur fractures without a traction table.
- Precision in locating the guide wire entry point.
- Optimization of positioning in the lateral view with a parallelism guide.
- Technique for fixing sliding and locking screws.
- Minimally invasive approach for early weight-bearing.
Detailed Content:
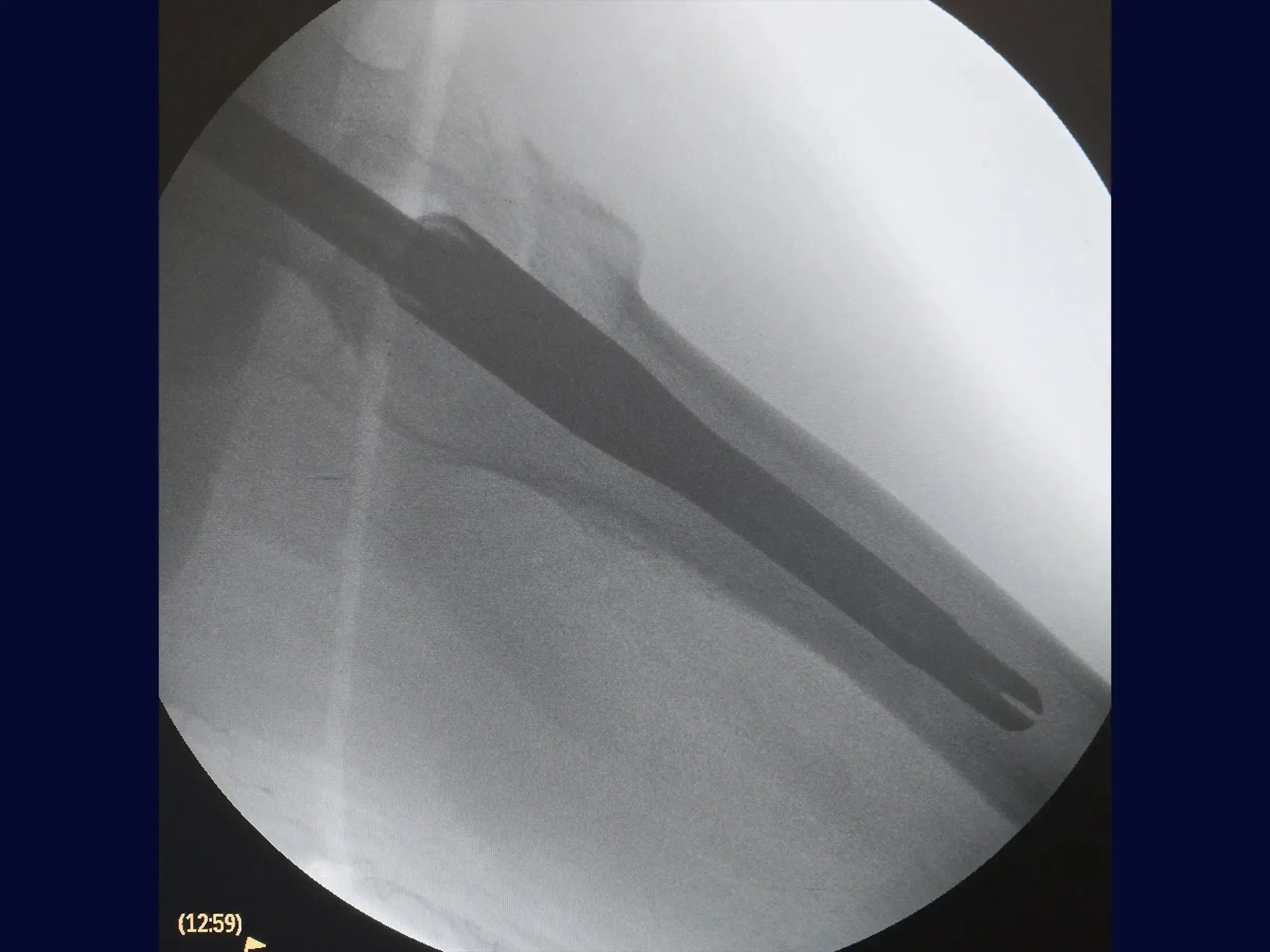
- Positioning and Guide Wire: Learn to position the patient without a traction table and identify the entry point of the guide wire using an image intensifier, adjusting for the patient's BMI. Insert the wire guided by the AP view and confirm in the medullary canal with leg rotation.
- Lateral Optimization and Rod: To correct the lateral positioning of the wire, use a parallelism guide that centers the wire in the medullary and femoral canal, avoiding obliquity of the sliding screw. Open the medullary canal with a drill and soft tissue protector, and introduce the short intramedullary rod.
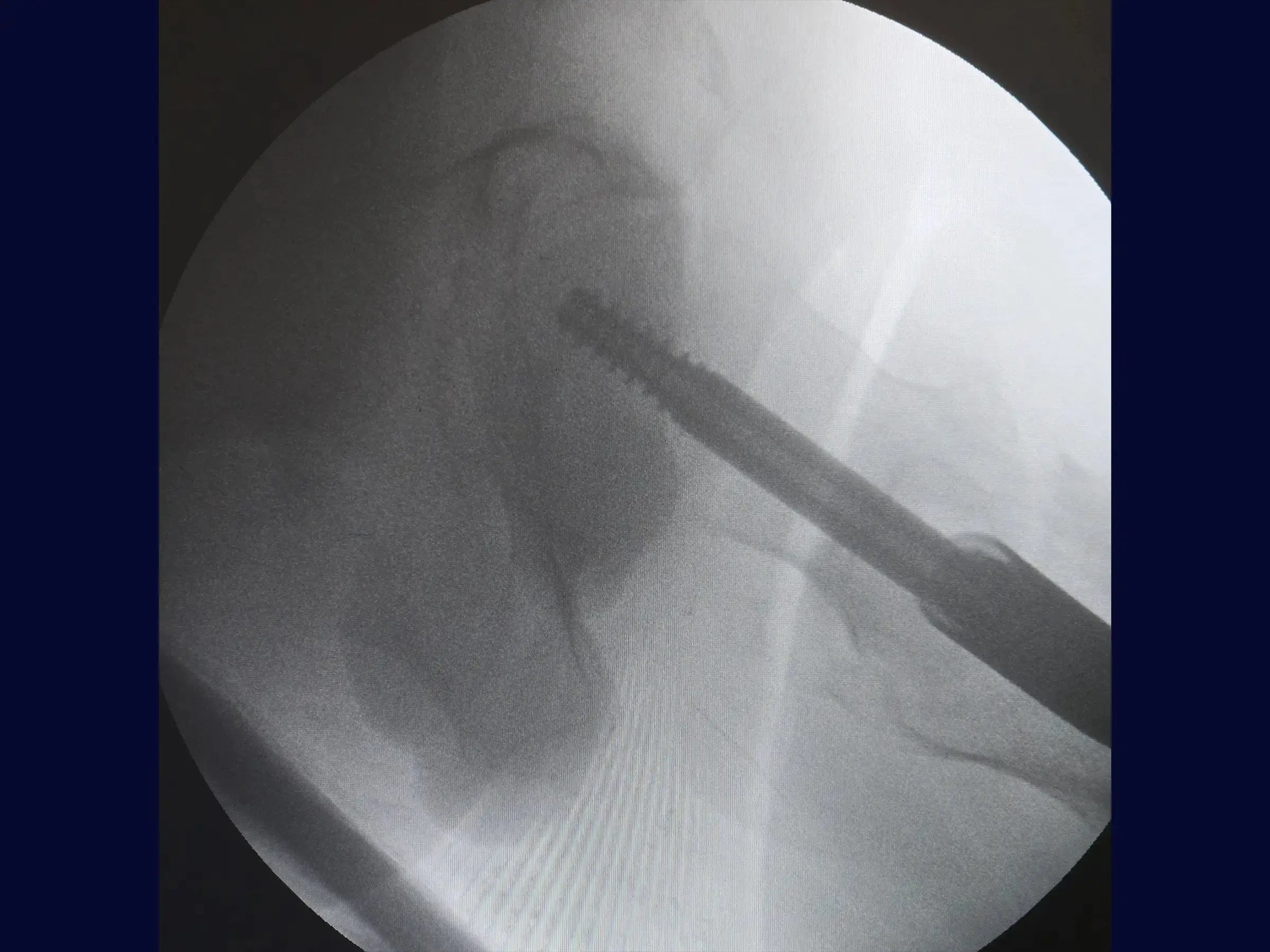
- Insertion of Screws: Make a minimally invasive lateral opening for the guide wire of the sliding screw, confirming its direction towards the center of the femoral head in both views. Measure and insert the sliding screw, using a second guide wire to prevent its retraction.The distal locking is guided by the introducer of the rod, with an incision of 1.5 cm. Ensure that the sliding screw allows for piston action.
- Results: The fracture is anatomically reduced, with the implant well positioned. The minimally invasive surgery allows for early weight-bearing support for the elderly patient.
Included Material:
- Detailed PDF: Covers everything from the positioning and entry point of the guide wire, optimization of positioning in the lateral view, opening of the medullary canal, insertion of the rod and sliding screw, to distal locking and finalization. It also includes a practical summary with the key points of the technique.
Transform your practice in proximal femur surgery. Sign up now and master the technique to operate on intertrochanteric fractures without a traction table, optimizing your procedures and results.

