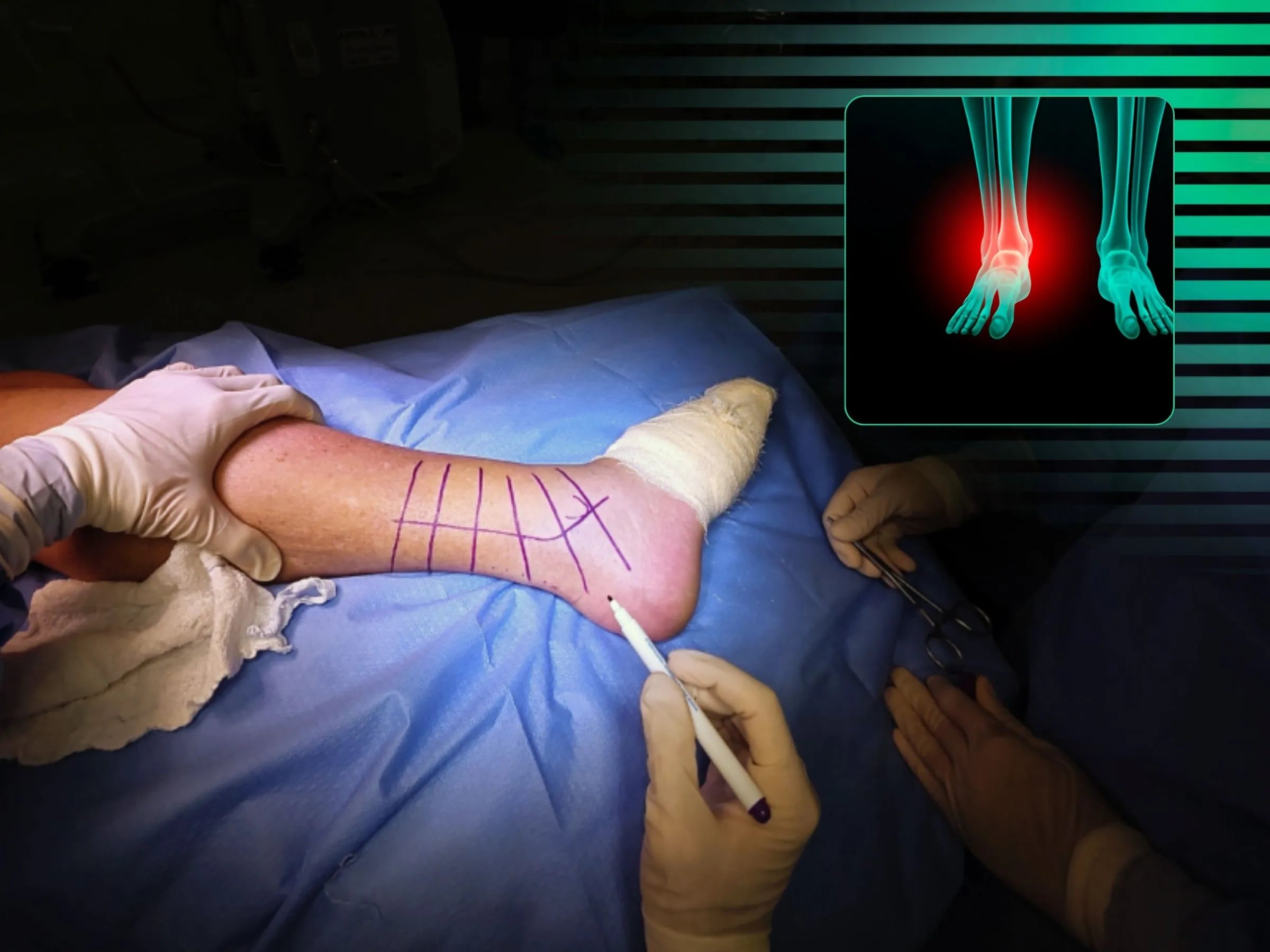
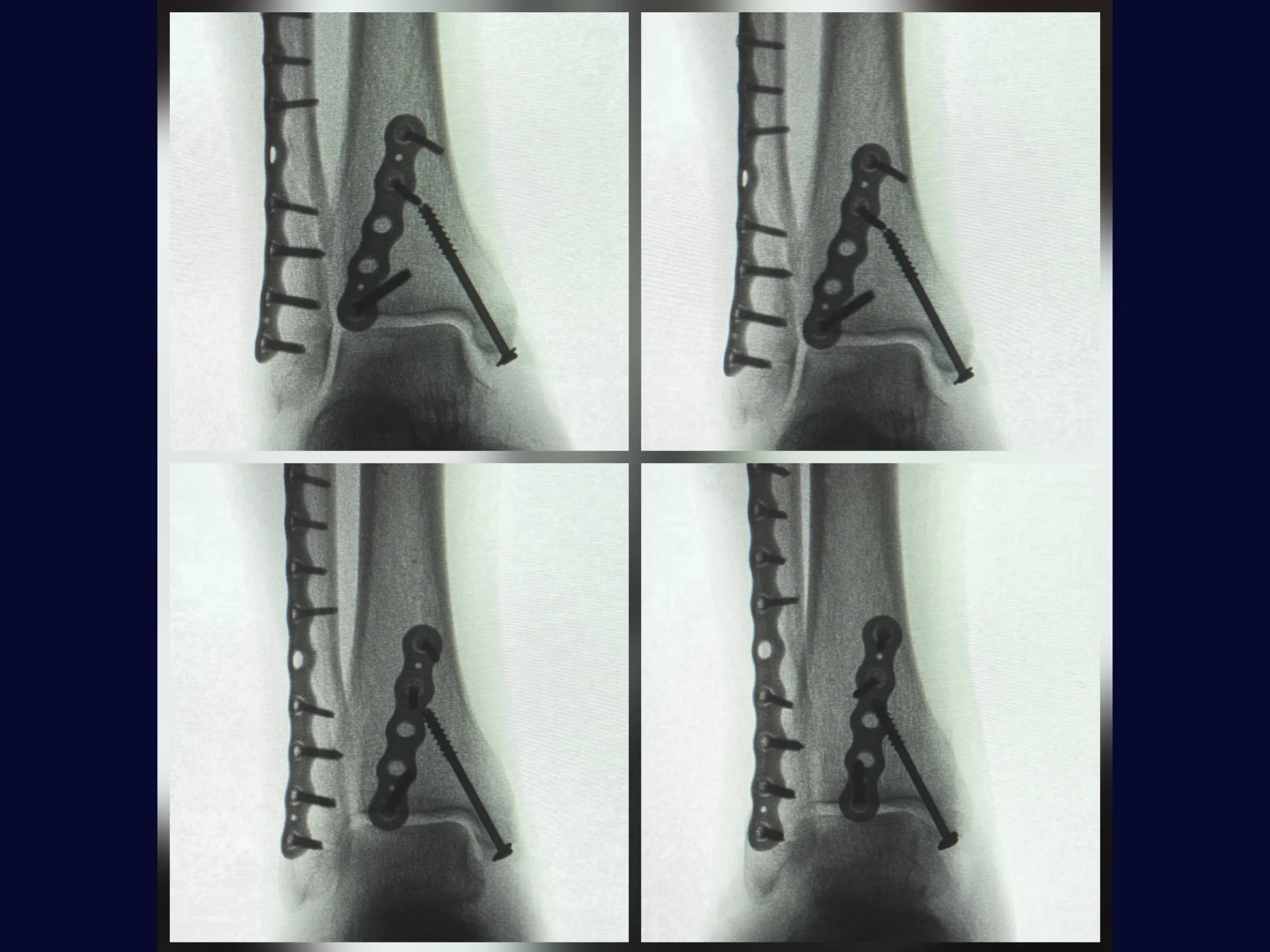
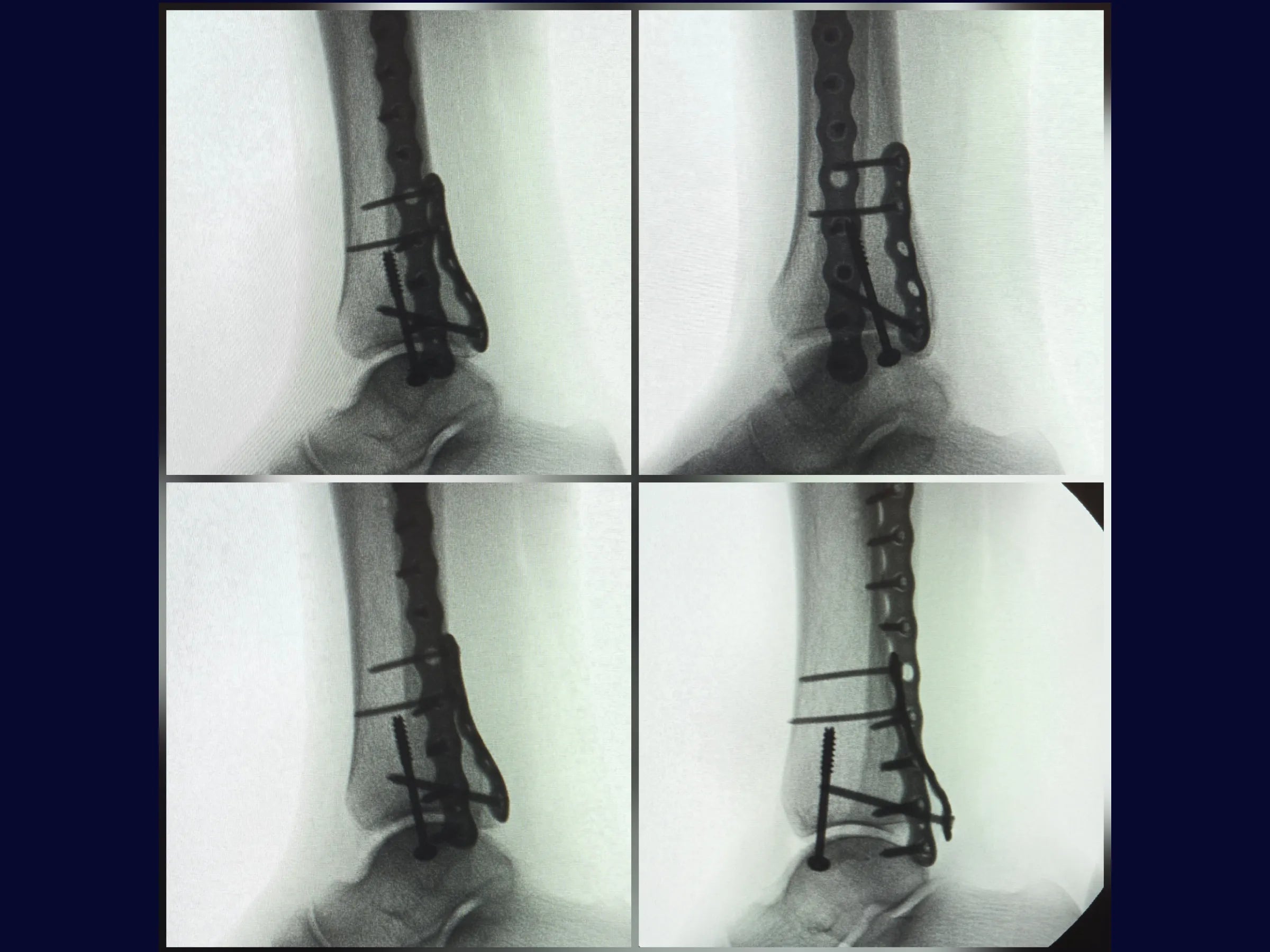
Trimalleolar Fracture - Lateral Decubitus Approach
Surgical precision in trimalleolar fractures: lateral approach and complete 4K stability.


4k videos
Professional Dubbing
Escolher opções











Description
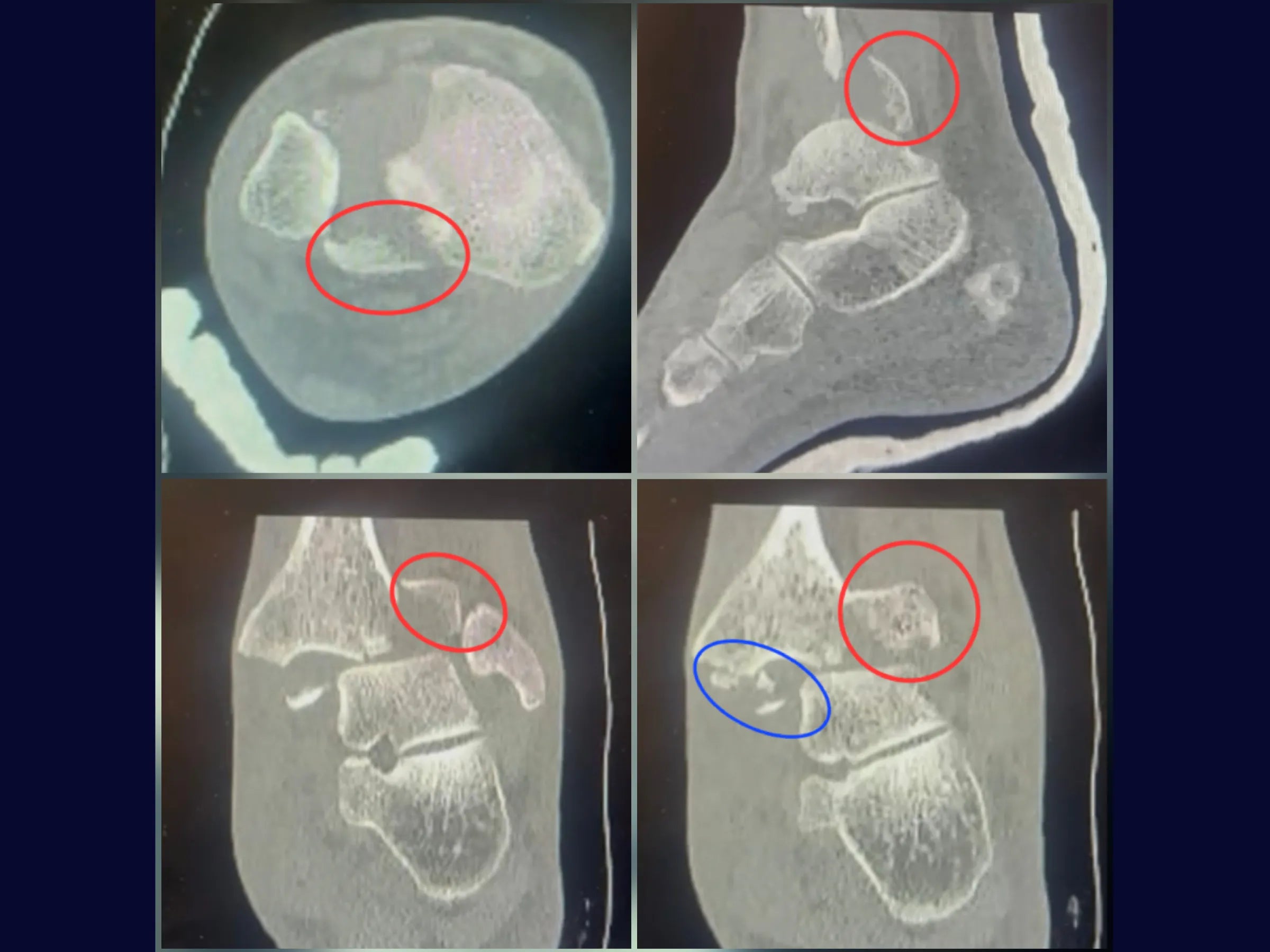
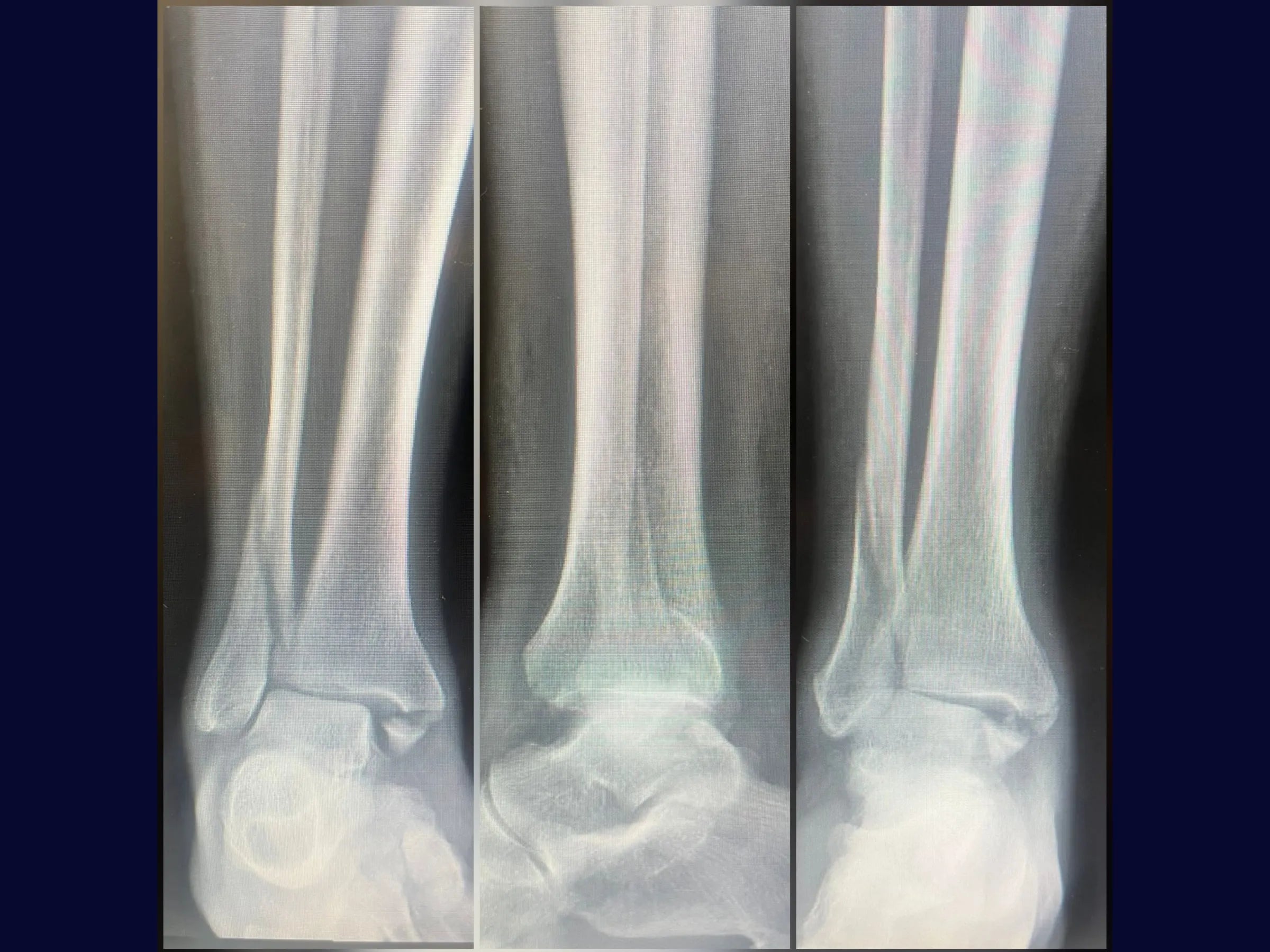
Trimalleolar fractures present a challenge due to their anatomical complexity and the need for complete joint stability. This training demonstrates, in 4K video from the surgeon's perspective, the systematic approach to reduction and fixation of the three malleoli, ensuring 360° stability and functional recovery.
Training Focus:
- Strategic positioning in lateral and supine positions.
- Posterolateral approach to the fibula and posterior malleolus.
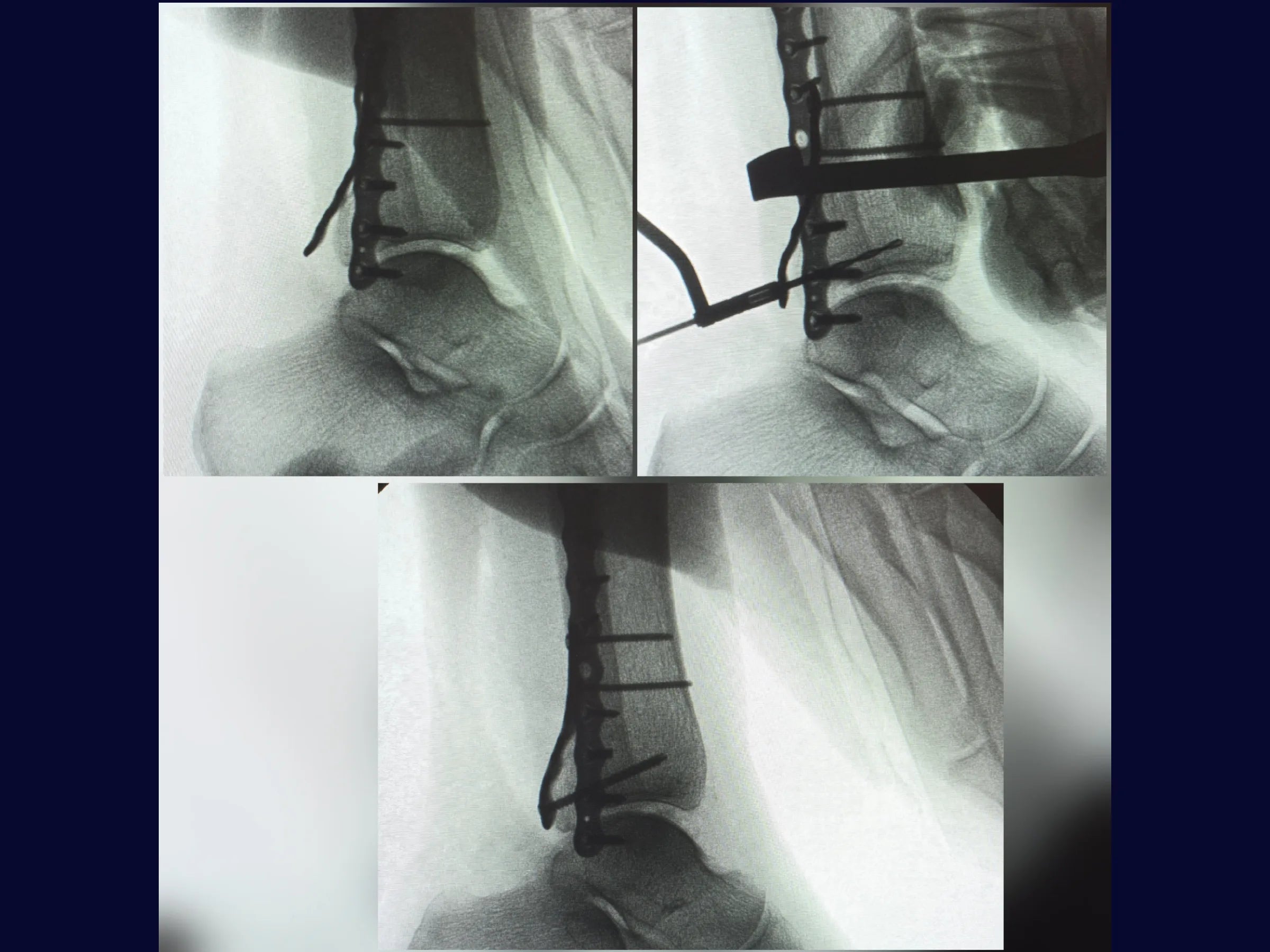
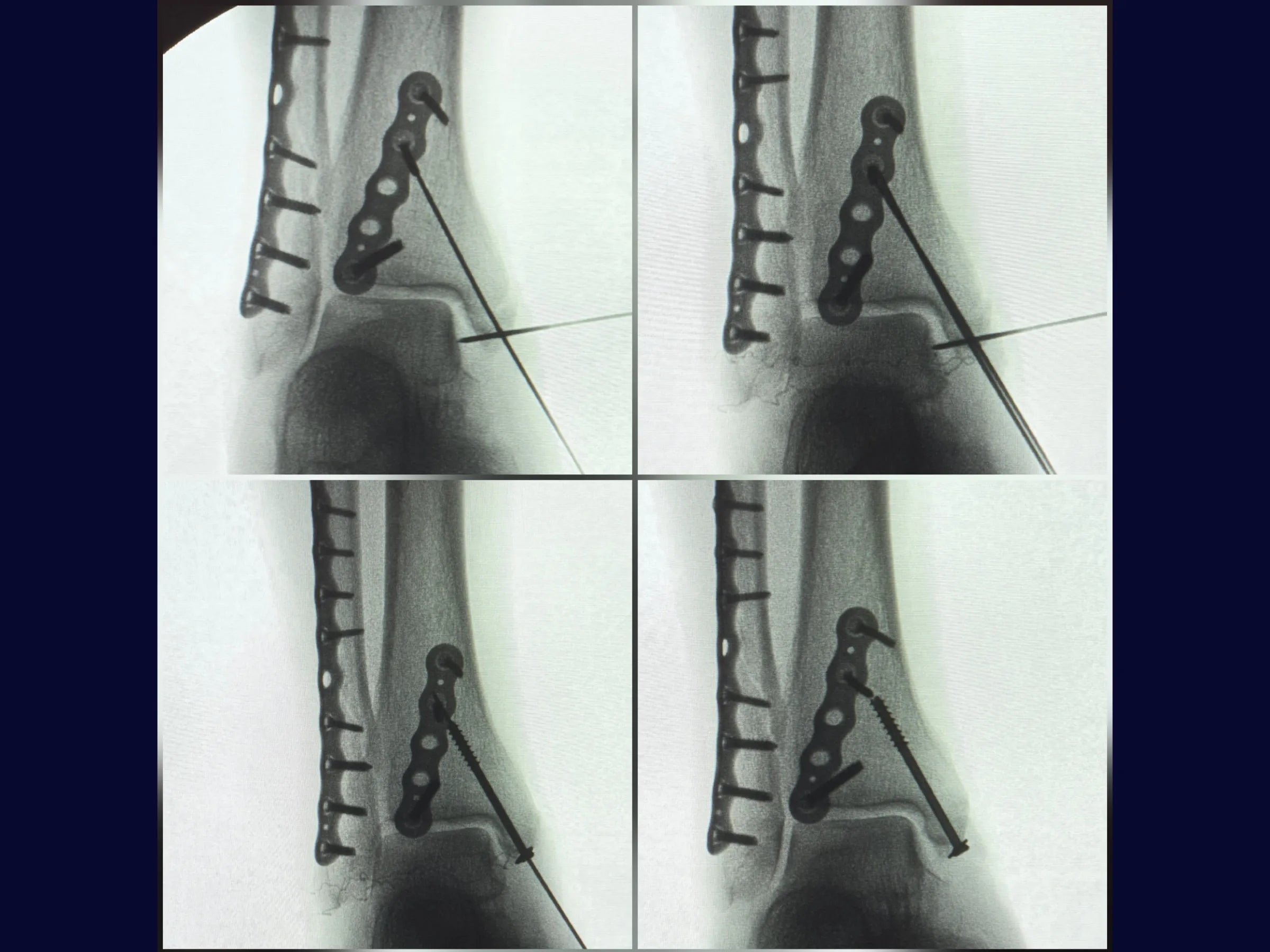
- Lateral malleolus fixation with a low-profile locking plate.
- Indirect reduction and fixation of the posterior malleolus with a shaped plate.
- Medial approach using a joystick wire and cannulated screw with washer.
Detailed Content:
- Anatomical Fibula Reduction: Use of fragment vertices and pointed forceps for length gain.
- Secure Fibular Fixation: Plate aligned with the shear vector, ensuring compression and stability.
- Posterior Anti-Shear Stabilization: Technique with key screw and controlled dorsiflexion.
- Low-Profile Implant: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and preserves vascularization.
- Biological Preservation: Minimal removal of the periosteum and careful dissection.
- Precision Medial Fixation: Use of a joystick wire for rotational control and a cannulated screw with a washer for final compression.
- Radiographic Control: Intraoperative check using an image intensifier.
- Safe Positioning Sequence: Lateral-to-dorsal conversion without risk of contamination.
Materials Included:
Detailed PDF: Contains an objective description of the technique, positioning sequence, approaches and fixations, as well as practical protocols for tissue preservation, use of low-profile implants, and strategies for 360° joint stability.
Improve your precision in fixing trimalleolar fractures. Enroll now and master the combined approach techniques for the lateral, posterior, and medial malleoli.

