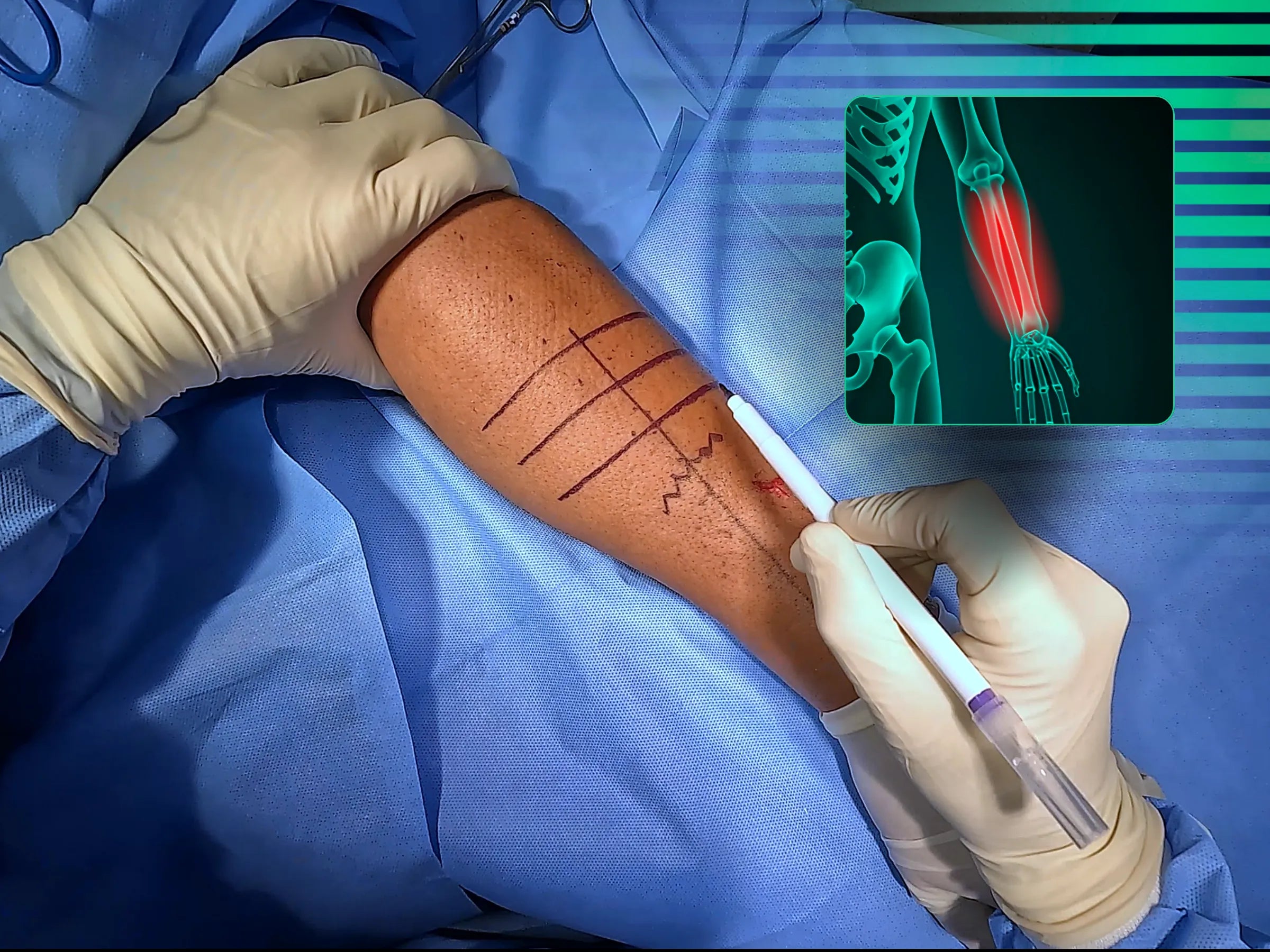
Diaphyseal Fractures of the Radius and Ulna
Master the repair of radius and ulna fractures with immersive surgical perspective in 4K.

Dr. Savio Chami
Médico Ortopedista
Available at::





4k videos
Professional Dubbing
Escolher opções




Diaphyseal Fractures of the Radius and Ulna
Preço promocionalR$ 0,00
Questions & Answers loading...
Description
Master the surgical treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna with this comprehensive training. Explore surgical approaches that emphasize anatomical preservation and clean technique, from planning and access to reduction and fixation, aiming to optimize patient recovery.
Training Focus:
- Surgical treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna.
- Dorsal approach (Thompson) for the radius fracture.
- Traditional approach for the ulna fracture.
- Anatomical reduction and stabilization of the fracture.
- Tissue preservation and minimization of bleeding.
Detailed Content:
-
Treatment of the Diaphyseal Radius Fracture (Thompson Approach):
- Planning and Marking: Learn to mark and palpate the Lister tubercle and the lateral epicondyle, drawing a line between them. Use muscle palpation to define the exact location of the skin incision and the imaging intensifier to locate the fracture site.
- Incision and Dissection: Master the skin incision with electrocautery and hemostasis. Deepen the dissection to identify the muscle intervals, using gauze for blunt dissection and visualizing the fascia for the ideal access plane, preserving the natural planes of the forearm.
- Fascia Opening and Exposure: Make a small incision through the fascia, creating the interval between the common extensor of the fingers and the short radial extensor of the wrist, with careful progression to preserve underlying structures and prevent muscle damage.
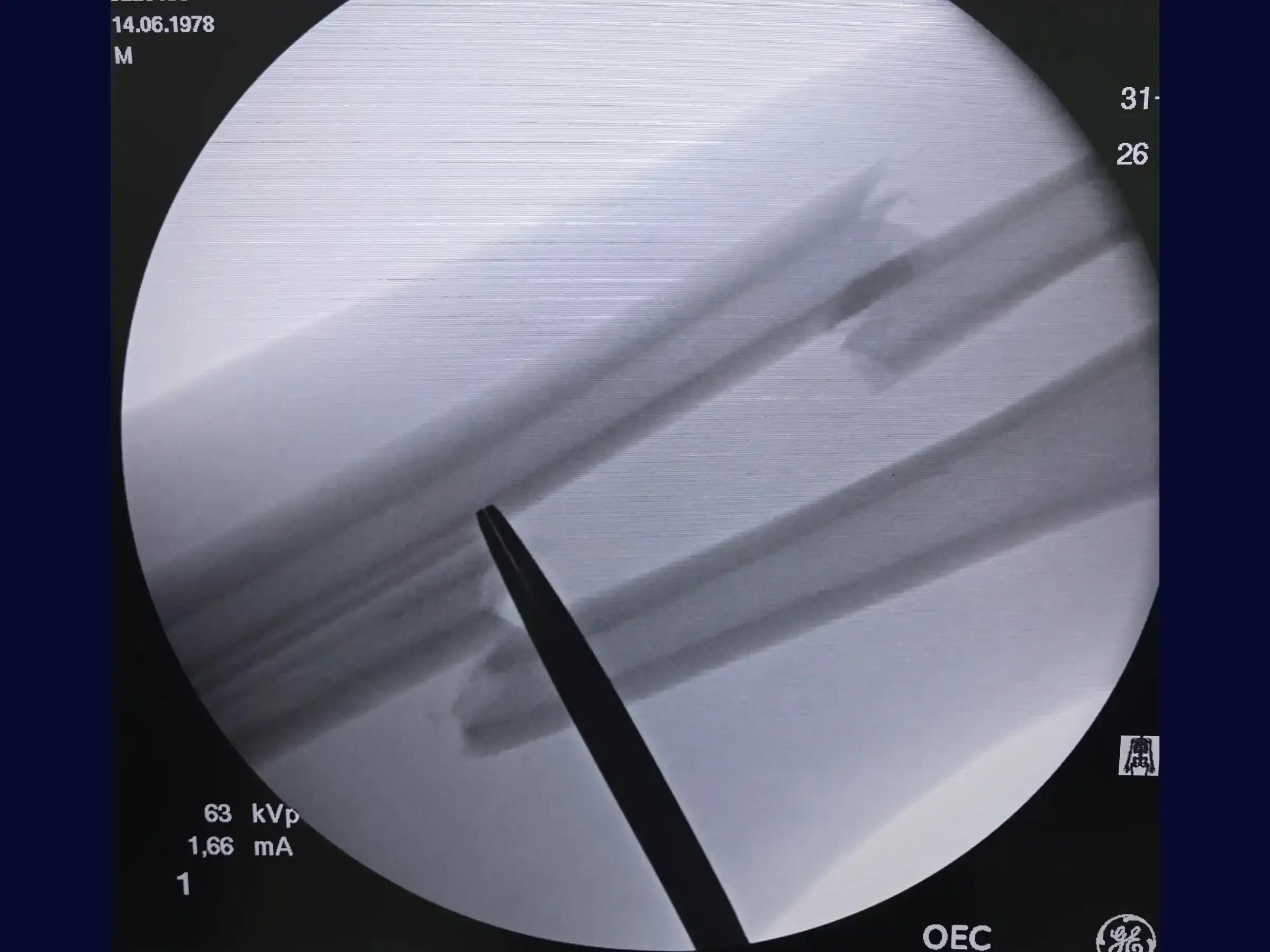
- Fracture Identification and Cleaning: Palpate the proximal fragment of the radius and define the trajectory towards the bone with your index finger.Make gentle contact with the scalpel on the bony surface to locate the apex and the proximal fragment, maintaining dissection along the anatomical planes and exposing the fracture ends. Clean the fracture edges to find a reference point for reduction.
-
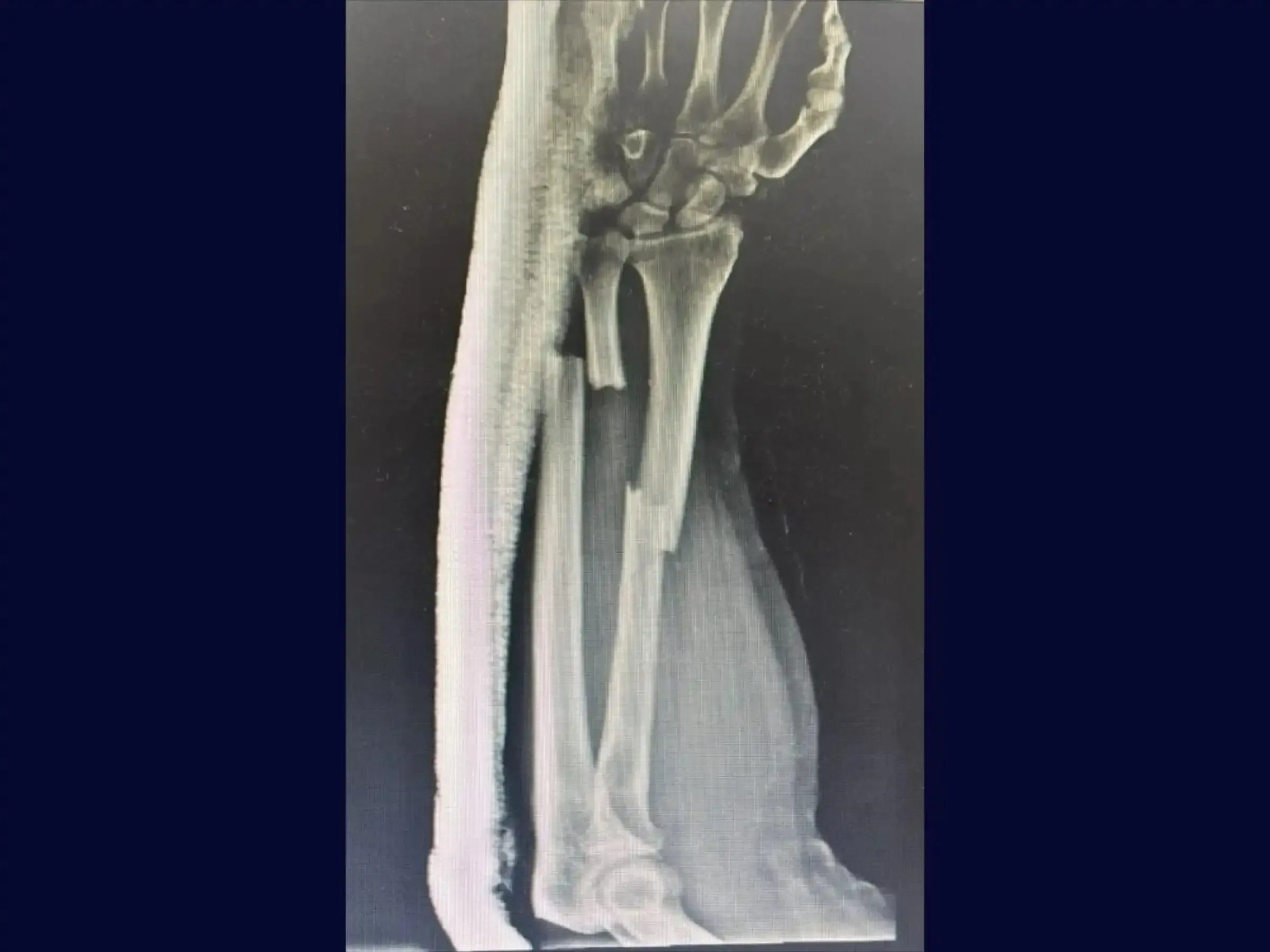
Treatment of Diaphyseal Fracture of the Ulna (Distal Third):
- Positioning and Access: Position the patient in a supine position with the arm flexed. Perform dissection between the extensor carpi ulnaris and flexor carpi ulnaris muscles, carefully opening the fascia to avoid muscle damage.
- Identification of the Fracture and Preservation of the Periosteum: Identify the fracture, even with distorted anatomy. Elevate the periosteum anatomically to minimize trauma to the soft tissues and facilitate closure over the plate.
- Bone Bed Preparation and Reduction: Create the bone bed precisely on the dorsal (tension) cortex of the ulna. Clean the fracture edges in search of reference points, using a "bony crest" as a guide for anatomical reduction and avoiding the creation of segmental fracture.
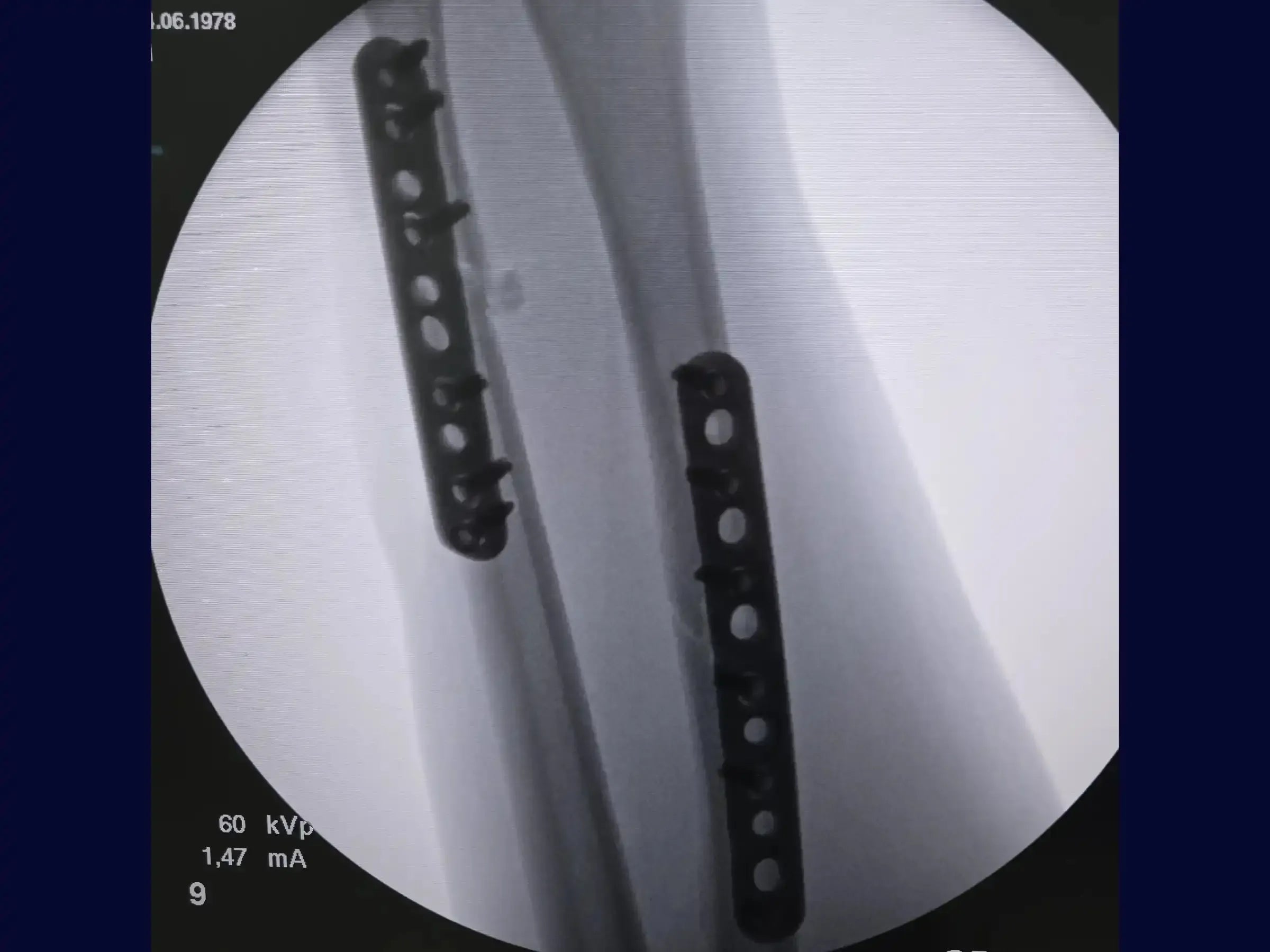
- Stabilization and Plating: Reposition the reduction clamp distally to optimize manipulation. With the radius already stabilized, achieve the reduction of the ulna for excellent stability and alignment. Perform plate pre-tensioning to avoid gap on the opposite cortex and use a 3.5 mm locked DCP (Dynamic Compression Plate).
- Closure and Recovery: Close the periosteum over the plate, preserving all muscle structures.Respect the anatomical dissection with total muscle preservation and perform closure in layers for a significantly improved postoperative recovery.
Included Material:
- Complete Technical PDF: A detailed educational document that addresses surgical techniques for the treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the radius (Thompson approach) and the ulna (traditional approach). It includes everything from initial planning and access to reduction and fixation of the fragments.
Enhance your skills in forearm surgery. Enroll now and master advanced osteosynthesis techniques for diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna, ensuring anatomical reduction and optimized recovery for your patients.

